The Qing Dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China, existing for 276 years from 1636 to 1912. During its peak, under the leadership of the Qing emperors, the nation expanded significantly, with a population that grew from 150 million to 450 million people. This era was also marked by substantial advancements in culture and the arts.
The Qing Dynasty saw 12 emperors, with the ruling lineage being the Aisin Gioro clan. This period is noted for the deep cultural integration between the Manchu and Han Chinese peoples, which significantly influenced Chinese society at the time. On February 12, 1912, Emperor Puyi abdicated, marking the end of the Qing Dynasty.
Today, through AI technology, we can visualize the likenesses of the Qing emperors, from the founding emperor Nurhaci to the last emperor Puyi.
AI Revives the Likeness of Qing Dynasty Emperors
Nurhaci – The Founder of the Qing Dynasty
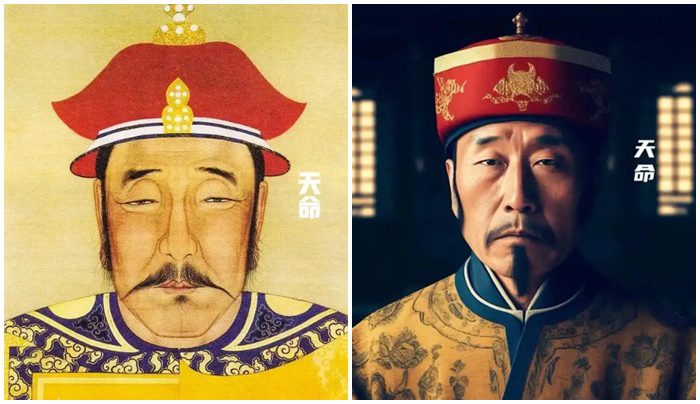
Nurhaci (also known as Tianming Emperor) reigned from 1616 until 1626. He was a prominent leader of the Jurchen tribes during the late Ming Dynasty. He is recognized for unifying the Jurchen tribes and establishing the Later Jin state, which laid the foundation for the future Qing Dynasty. His efforts were pivotal in the eventual rise of the Qing and the consolidation of power between the Jurchens and Han Chinese.
AI-generated images of Nurhaci present a striking representation compared to historical depictions.

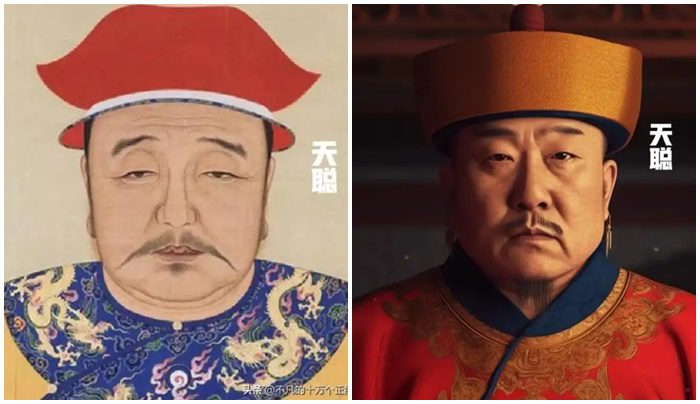
Hong Taiji
Hong Taiji (also known as Tianzhong Emperor) reigned from 1626 until 1636 (deposed in 1636) and from 1636 until 1643 (as emperor for 8 years). He was the son of Nurhaci and continued to strengthen the unification between the Manchu and Han peoples. During his reign, he implemented significant reforms, including establishing the policy of “harmonious governance” and the standardization of laws and currency. His reign solidified the foundations for the prosperity and stability of the Qing Dynasty.
The AI-generated image of Hong Taiji presents a dignified portrayal, capturing the essence of his leadership.

Shunzhi
Shunzhi reigned from 1644 until 1661. He was the first emperor of the Qing Dynasty after its conquest of China. Throughout his reign, Shunzhi faced numerous challenges, including wars against the Ming loyalists, natural disasters, and internal strife. Nevertheless, he succeeded in consolidating the power of the Qing Dynasty and ushered in the Kangan era.
The AI-generated likeness of Shunzhi presents him in a youthful state, embodying the vigor of his early reign.

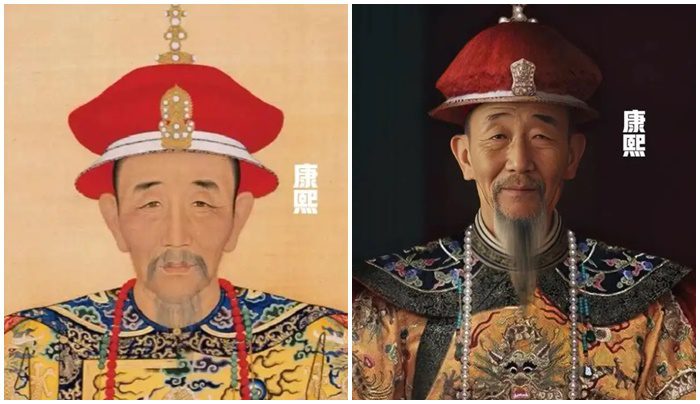
Kangxi
Kangxi reigned from 1661 until 1722. He was the son of Shunzhi. During his reign, Kangxi implemented substantial reforms, including aggressive land reclamation and restructuring the bureaucracy. His era established a strong foundation for the prosperity and stability of the Qing Dynasty.
The AI-generated portrayal of Emperor Kangxi evokes a sense of majesty, reflecting his influential reign.

Yongzheng
Yongzheng reigned from 1722 until 1735. He was the son of Kangxi. Yongzheng implemented significant reforms, including the establishment of the “centralized government” and financial reorganization. His reign contributed to the strengthening of the Qing Dynasty and its governance.
The AI-generated image of Yongzheng presents him as a resolute leader, embodying the authority of his rule.
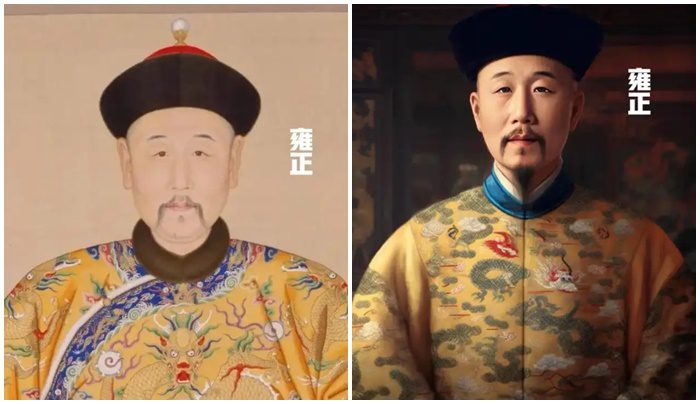

Qianlong
Qianlong reigned from 1736 until 1796. He was the son of Yongzheng and presided over the Qing Dynasty at its zenith. He implemented various reforms, including the policy of “cultural enrichment” and strengthened border management. His reign is celebrated as a peak period of the Qing Dynasty.
The AI-generated image of Qianlong shows him with a vibrant and dynamic presence, contrasting with traditional portrayals.

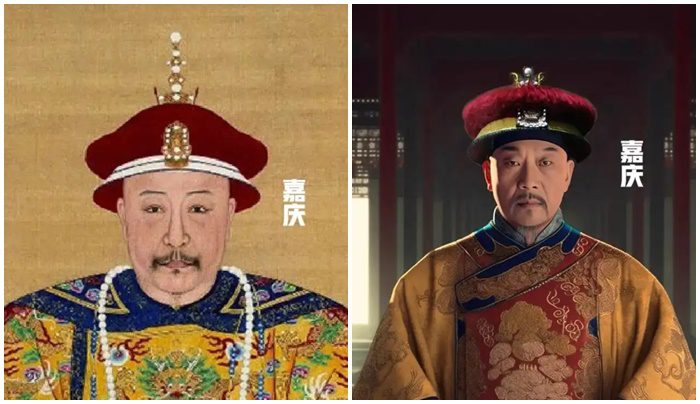
Jiaqing
Jiaqing reigned from 1796 until 1820. He was the son of Qianlong and faced numerous social issues and corruption during his rule. Despite his efforts to enact reforms, he struggled to achieve significant success.
The AI-generated image of Jiaqing presents him as a strong figure, differing from his historical likenesses.

Xianfeng
Xianfeng reigned from 1850 until 1861. He was the son of Jiaqing, facing severe challenges during his reign, including the Taiping Rebellion and the Second Opium War. Despite attempts at reform, he was unable to overcome the crises of his time.
The AI-generated depiction of Emperor Xianfeng evokes a sense of solemnity, reflecting the tumultuous nature of his reign.

Tongzhi
Tongzhi reigned from 1862 until 1875. He was the son of Xianfeng and was the last emperor of the Qing Dynasty to hold actual power. He attempted various reforms but faced strong opposition from conservative factions and ultimately could not succeed.
The AI-generated image of Tongzhi presents him as a figure of determination amidst his struggles.

Guangxu
Guangxu reigned from 1875 until 1908. He was the younger brother of Tongzhi and faced immense pressure both internally and externally, as well as significant challenges regarding the financial stability of the Qing Dynasty. He attempted various reforms but faced strong opposition and could not succeed.
The AI-generated image of Guangxu presents him as a thoughtful and introspective ruler.

Puyi
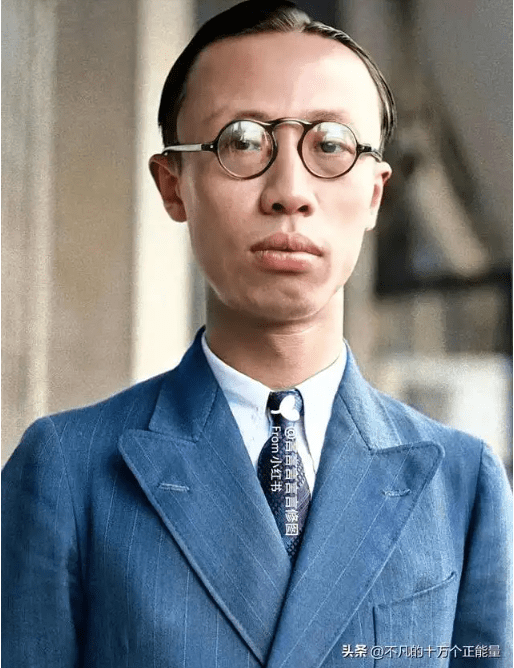

Puyi reigned from 1909 until 1912. He was the last emperor of the Qing Dynasty and faced immense pressure internally and externally, along with significant financial challenges. He made efforts to implement several reforms, such as increasing local governance authority and easing burdens on the populace. However, these efforts were insufficient to address the issues facing the dynasty. Ultimately, he was forced to abdicate during the Xinhai Revolution, marking the end of the Qing Dynasty.